Introduction:
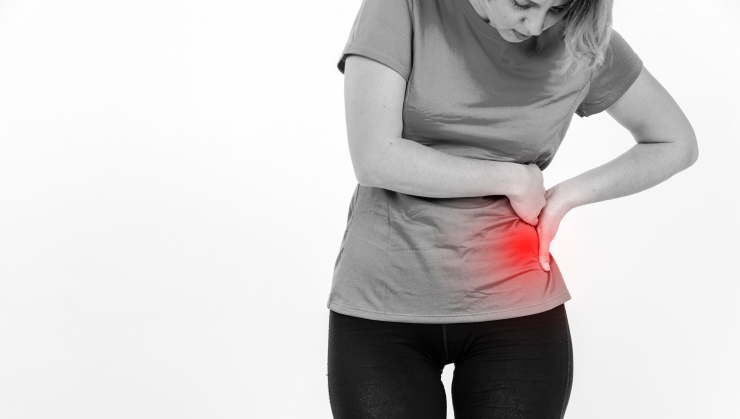
Pelvic pain, which refers to discomfort or pain in the lower abdominal region, can be a distressing and disruptive symptom for both men and women. It can range from mild and intermittent to severe and chronic. Understanding the causes and available treatment options is essential for those experiencing pelvic pain. In this article, we will explore the common causes of pelvic pain and the various treatment options to alleviate this discomfort.
Common Causes of Pelvic Pain:
-
Menstrual Pain (Dysmenorrhea): Many women experience pelvic pain during their menstrual cycles, known as dysmenorrhea. It is often due to uterine contractions as the body sheds the uterine lining.
- Ovulation Pain (Mittelschmerz): Some women experience mild discomfort or pain during ovulation when an egg is released from the ovaries.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs and is a common cause of pelvic pain. It can result from untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue lining the uterus (endometrium) grows outside of it. This can lead to severe pelvic pain, especially during menstruation.
- Fibroids:Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths in the uterus and can cause pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, and pressure in the lower abdomen.
- Ovarian Cysts: Cysts on the ovaries are common and can occasionally cause pelvic pain, particularly if they rupture or become twisted.
- Interstitial Cystitis:This chronic condition causes pain and pressure in the bladder area, resulting in pelvic pain.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS can cause abdominal pain, cramping, and discomfort that may radiate to the pelvic area.
- Bladder or Urinary Tract Infections: Infections in the bladder or urinary tract can cause pelvic pain and discomfort.
Treatment Options for Pelvic Pain:
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help alleviate mild to moderate pelvic pain.
- Hormonal Therapy: For conditions like endometriosis or fibroids, hormonal therapy, including birth control pills or hormonal IUDs, can help manage symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If pelvic pain is due to an infection, antibiotics can effectively treat the underlying cause.
- Physical Therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles and alleviate pain in cases of muscular or functional issues.
- Lifestyle Changes:Dietary adjustments, stress management, and regular exercise can help with pelvic pain caused by conditions like IBS.
- Surgery: In cases of severe or chronic pain, surgical procedures may be necessary to address the underlying issue, such as removing cysts or fibroids.
- Bladder Training: For conditions like interstitial cystitis, bladder training can help manage symptoms.
- Complementary Therapies:Some individuals find relief through complementary therapies like acupuncture, yoga, and meditation.
Conclusion:
Pelvic pain can result from various causes, and its treatment depends on the underlying condition. If you experience persistent or severe pelvic pain, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By identifying the cause of the pain and following a tailored treatment plan, many individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. Don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you are dealing with pelvic pain, as early intervention can often lead to more successful outcomes.