Introduction
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is a complex autoimmune disease that can affect various organs and systems in the body. It is characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential damage. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of SLE, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and management strategies.
Understanding the Basics: What is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus ?
SLE is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system, responsible for protecting the body, mistakenly attacks its tissues and organs. This can result in a range of symptoms and complications that vary in severity, making lupus a challenging condition to diagnose and manage.
Symptoms of SLE : The Many Faces of Lupus
Lupus can manifest in diverse ways, and its symptoms may come and go, often resembling other illnesses. Common symptoms include :
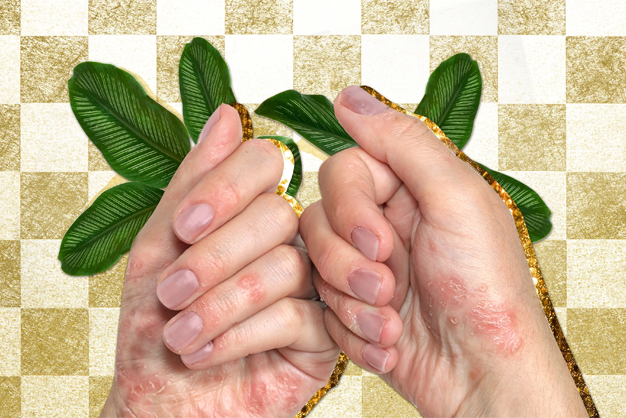
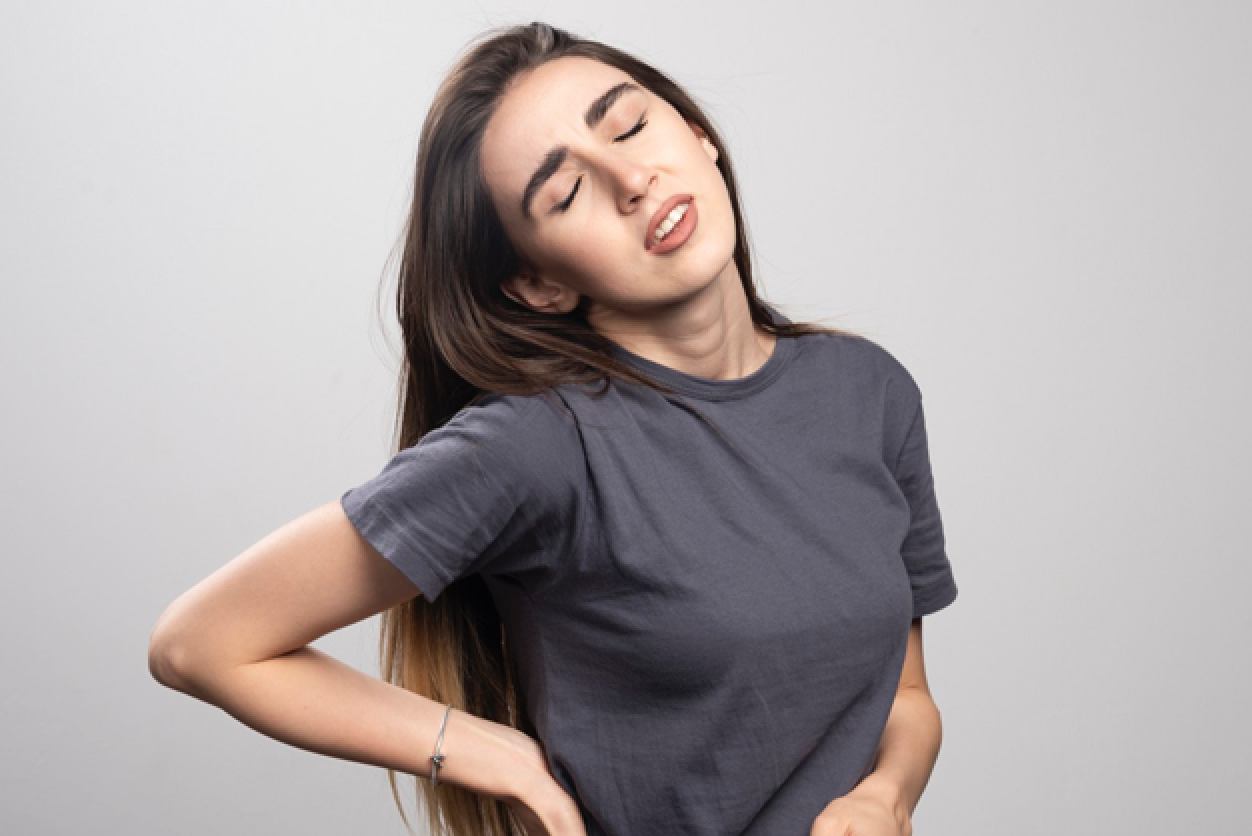
- Joint Pain and Swelling : Lupus often causes arthritis-like symptoms with pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints.
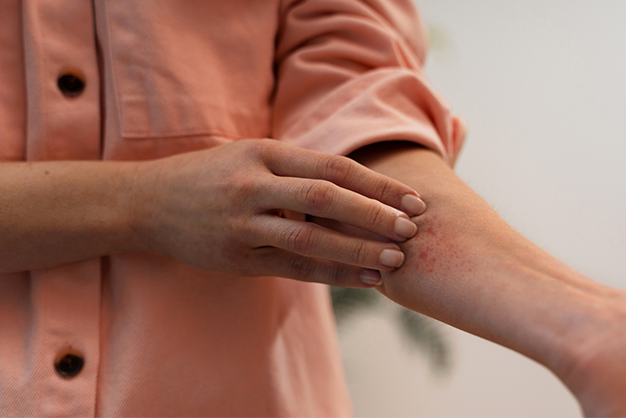
- Skin Rashes : The classic butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose is a hallmark of lupus, but other skin rashes can also occur.
- Fatigue : Persistent and overwhelming fatigue is a common complaint among individuals with lupus.
- Organ Involvement : Lupus can affect internal organs such as the kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain, leading to a variety of complications.
- Photosensitivity : Increased sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in skin reactions.
Causes and Triggers : Unraveling the Lupus Puzzle
The exact cause of SLE remains unclear, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors is believed to contribute. Potential triggers for lupus flares include :
- Environmental Factors : Sunlight exposure, infections, and certain medications can trigger lupus flares.
- Genetic Predisposition : Individuals with a family history of lupus may have a higher risk
- Hormonal Influences : Lupus is more common in women, and hormonal factors may play a role.
Diagnosis and Treatment : Partnering with Healthcare Professionals
Diagnosing lupus can be challenging due to its varied and often elusive symptoms. Healthcare professionals use a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to arrive at a diagnosis.
- Medications : Treatment often involves medications to control symptoms and manage inflammation, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Immunosuppressants : In severe cases, medications that suppress the immune system may be prescribed to reduce the autoimmune response.
- Lifestyle Changes : Managing stress, getting adequate rest, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are crucial for individuals with lupus.
Living with Lupus : Coping Strategies and Support
Living with lupus requires a holistic approach that extends beyond medical interventions :
- Self-Care : Prioritizing self-care, including adequate sleep, a balanced diet, and regular exercise.
- Mental Health Support : Dealing with a chronic illness can be emotionally challenging, and seeking support from mental health professionals or support groups can be beneficial.
- Regular Monitoring : Continuous communication with healthcare providers, regular check-ups, and monitoring of symptoms help manage lupus effectively.
Conclusion
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus presents a complex and often unpredictable journey for those affected. While there is no cure, advancements in medical understanding and treatment options offer hope for improved management and quality of life. With a combination of medical intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing support, individuals with lupus can navigate the complexities of this autoimmune disease and strive for a fulfilling and resilient life.
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)